Metal Perimeter Edge Testing FAQs
Please review our ANSI/SPRI ES-1 reference information for answers about our metal roofing edge testing services. By adhering to ANSI/SPRI ES-1 standards, builders are assured that their building’s roofing perimeter edging will comply with local building codes and International Building Codes. For additional assistance, please call 844-WTSC-ES1 to speak to a Wind Testing Services Corporation representative.
What is ANSI/SPRI ES-1?
It is a standard for those who design, specify, or install edge materials used with low slope roofing systems. The standard defines a formula that determines roof edge design pressure. It also describes three specific test protocols that are to be applied to copings and horizontal roof edges.
What does this mean for me?
It is very likely that your project is required to include ANSI/SPRI ES-1 tested perimeter edge flashings. Roofs with edges designed and installed to meet ES-1 provide wind securement in the most vulnerable area of the roof: the edge! Contact Wind Testing Services Corporation today to learn how you can save money + meet code requirements on your low slope roof projects.
How long do WTSC certifications last?
Your certification will last for one year. Optionally, WTSC can perform a yearly audit of your facility to ensure that the tested flashing(s) continue to be manufactured in the same manner as the original tested part.
I’ve designed a custom part(s) for a project. Can you test it?
Yes! Contact us today to get started on the way to certification! It’s a simple process:
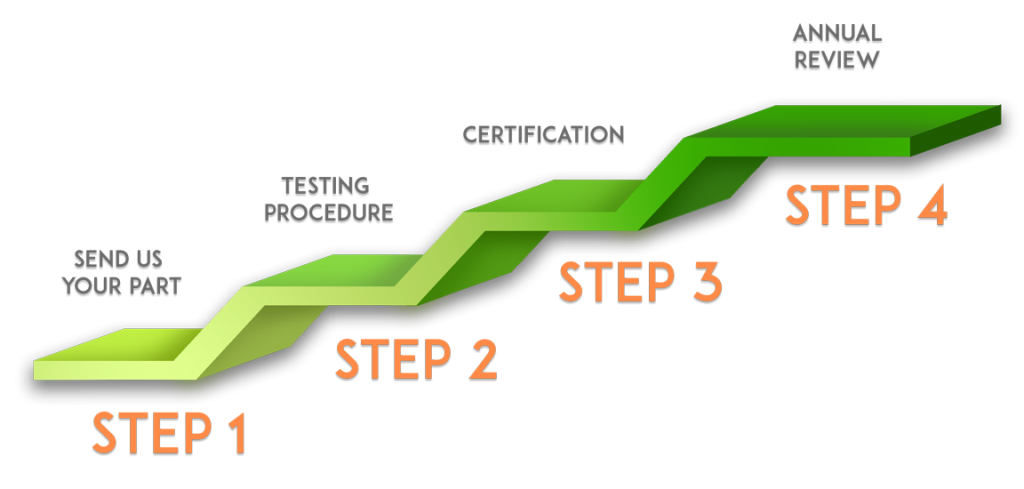
I think my flashings will meet the required wind load and withstand ES-1 tests, but what if they don’t?
Please Contact us for more details.
Who and what are ANSI, SPRI, FM Global, ICC, IBC?
ANSI: The American National Standard Institute (ANSI) is a non-profit organization that administers and coordinates voluntary standardization systems.
SPRI: The Single-Ply Roofing Industry (SPRI) is a non-profit trade association representing sheet membrane and component suppliers to the commercial roofing industry. SPRI is an official ANSI canvasser and has worked with representatives of the roofing industry to develop a number of standards.
FM Global: FMGlobal provides commercial and industrial property insurance and risk management solutions.
ICC/IBC: The International Code Council (ICC) is a non-profit organization that works to develop comprehensive and coordinated national construction codes. It has developed the International Building Code (IBC), which provides a consensus standard for construction codes.
Why are all of these organizations involved in setting roofing industry standards?
Prior to 1980 there were no roofing perimeter edge standards by which manufacturers could hold themselves to. FM Global then created a system of standards and approvals to use on FM Global insured properties. The design community adopted this system because there were no other available standards at the time.
In 1998 SPRI developed three tests to judge the quality and durability of fascias and copings. These tests were incorporated into a wind load test standard known as “Wind Design Standard for Edge Systems Used with Low Slope Roofing Systems”. This testing standard has since been accepted by ANSI as a national test standard for low slope roof edge systems. The standard, known as ANSI/SPRI ES-1, was adopted into the 2003 IBC.
How does the IBC code actually read?
The 2012 IBC states: “1504.5 Edge securement for low-slope roofs. Low-slope built-up, modified bitumen and single-ply roof system metal edge securement, except gutters, shall be designed and installed for wind loads in accordance with Chapter 16 and tested for resistance in accordance with Test Methods RE-1, RE-2 and RE-3 of ANSI/SPRI ES-1, except Vult wind speed shall be determined from Figure 1609A, 1609B, or 1609C as applicable.”
Which areas have adopted the 2003 or later IBC?
All 50 states have adopted some version of the IBC. The majority of states have adopted 2006 or later versions, which include ANSI/SPRI ES-1 compliance.
What information is used the standard to determine the loads on a roof edge?
- Wind Speed
- Building Occupancy
- Building Height
- Building Location
- Location of the edge component on the roof
What other details are taken into consideration in the standard?
- Structural integrity of the nailer or other substrate that anchors the edge
- Membrane attachment method
- Wind resistance of the edge details
- Metal thickness and galvanic compatibility of materials


